Xgrid Gravel Grid A Comprehensive Guide
Comparative Analysis of Gravel Stabilization Methods
Different gravel stabilization methods offer varying degrees of performance and cost-effectiveness. Understanding these differences is essential for making informed decisions.
Cost Comparison
| Feature | XGrid Gravel Grid | Alternative Method 1: Traditional Gravel Base | Alternative Method 2: Geotextile Fabric Reinforcement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Generally moderate, often competitive with traditional methods but potentially higher than geotextile reinforcement, depending on project scale and material costs. Installation costs can be lower in the long run due to reduced maintenance and potential for faster installation. | Relatively low initial cost, but ongoing maintenance can increase long-term expenditure. Cost per square foot is often lower than XGrid. | Lower initial cost than XGrid, typically the least expensive option. Long-term maintenance and potential for material degradation may increase costs over time. |
Durability
| Feature | XGrid Gravel Grid | Traditional Gravel Base | Geotextile Fabric Reinforcement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Durability | High durability, owing to the robust grid structure. The interlocking design resists deformation and displacement, ensuring long-term stability. The grid provides a strong base, even under heavy loads and traffic. | Durability is moderate; traditional gravel bases can settle or compact over time, potentially requiring periodic replacement or maintenance. Durability depends on the thickness and compaction of the gravel layer. | Moderate durability; geotextile reinforcement provides some stability but may not withstand the same level of stress as XGrid or traditional gravel bases. Long-term performance depends on the quality of the geotextile and the nature of the load. |
Installation Process
| Feature | XGrid Gravel Grid | Traditional Gravel Base | Geotextile Fabric Reinforcement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Installation | Installation is generally faster and more efficient than traditional methods, due to the prefabricated nature of the grid. Reduced labor time often translates to lower installation costs. The interlocking design facilitates faster assembly and precise placement. | Installation is labor-intensive, involving extensive compaction and grading of the gravel layer. Installation can be time-consuming and potentially require specialized equipment for proper compaction. | Installation is relatively simple and can be performed with standard equipment. However, ensuring proper geotextile placement and tension is crucial for effectiveness. Installation time can be comparable to XGrid, but it depends on the project size. |
Environmental Impact
| Feature | XGrid Gravel Grid | Traditional Gravel Base | Geotextile Fabric Reinforcement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | XGrid grids can be manufactured with recycled materials, offering a positive environmental footprint. Reduced material use and faster installation minimize waste and disturbance to the environment. The interlocking nature of the grid reduces the amount of gravel needed, further minimizing environmental impact. | Traditional gravel bases often involve significant extraction of natural resources, which can have a negative environmental impact. Maintaining the base requires potentially disruptive and resource-intensive processes. | Geotextile reinforcement may have a lower environmental impact than traditional gravel methods due to reduced material use, however, the production and disposal of synthetic materials still need to be considered. Potential for contamination and improper disposal of materials should be considered. |
Strengths and Weaknesses
| Feature | XGrid Gravel Grid | Traditional Gravel Base | Geotextile Fabric Reinforcement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strengths | High strength and stability, faster installation, reduced maintenance, potentially lower long-term cost, and suitability for various applications. | Low initial cost, readily available materials, and simplicity of implementation. | Cost-effectiveness, ease of installation, and suitability for some applications. |
| Weaknesses | Higher initial cost compared to some alternatives, and potential for material sourcing issues. | Susceptible to settlement and degradation over time, requiring periodic maintenance. May not withstand high loads or heavy traffic. | Limited load-bearing capacity, susceptibility to degradation, and potential for inadequate drainage if not properly installed. |
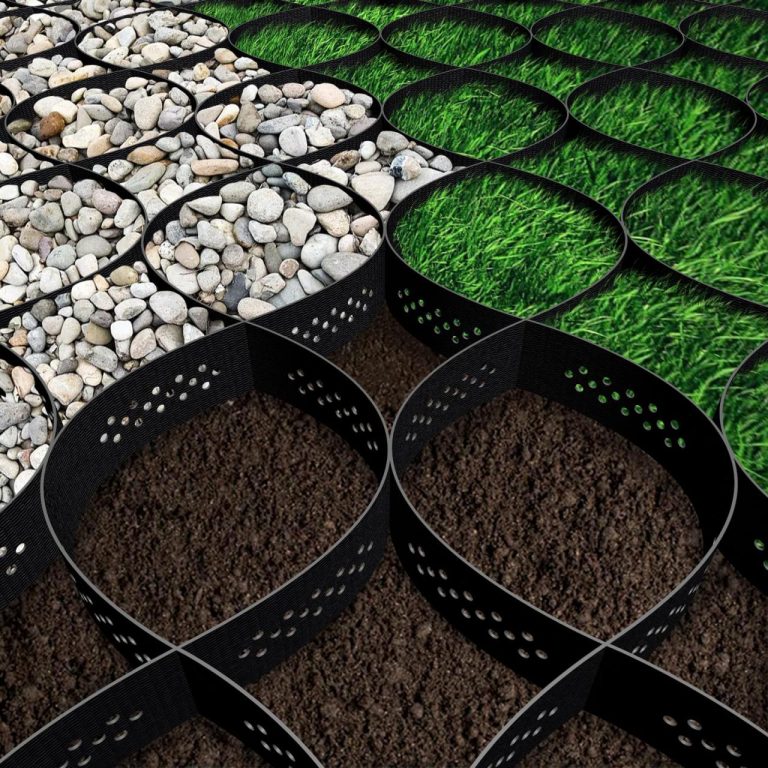
Xgrid gravel grids offer a versatile solution for various applications, from landscaping to road construction. This guide delves into the specifics of these innovative grids, covering everything from design and construction to maintenance and comparison with alternative methods. Understanding the key components, typical dimensions, and diverse applications will empower you to make informed decisions when considering this practical solution.
We’ll explore the advantages of XGrid gravel grids, highlighting their cost-effectiveness, superior drainage capabilities, and impressive durability. Further, we’ll investigate the step-by-step installation process, addressing potential challenges and offering solutions to ensure a smooth and successful project.
Introduction to XGrid Gravel Grids

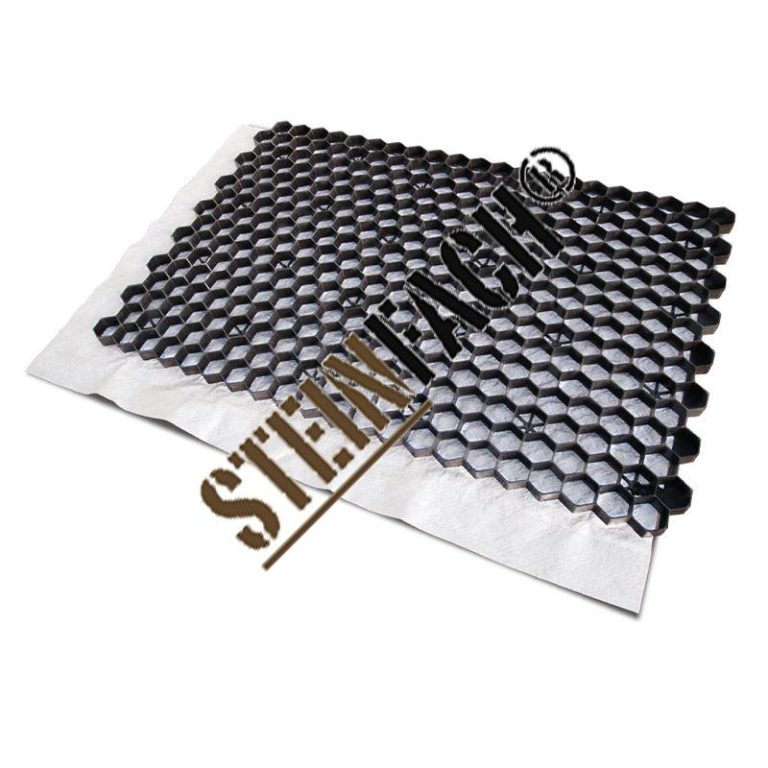
XGrid gravel grids are a reinforced pavement system designed for use in various applications where a stable and permeable surface is needed. They offer a cost-effective alternative to traditional concrete or asphalt paving, especially in areas with high traffic or where drainage is critical. Their modular design and versatility make them suitable for a wide range of projects.
These grids, composed of interlocking polymer or steel components, are overlaid with gravel, creating a strong and durable surface. This approach allows for water to drain through the grid, preventing waterlogging and promoting healthy drainage, crucial in areas prone to flooding or excessive rainfall. The design of the grid itself ensures a stable base, preventing settling or damage under heavy loads.
Key Components and Materials
XGrid gravel grids are primarily composed of interlocking polymer or steel grid units. These units are designed to interlock tightly, forming a stable network. The grid itself is overlaid with a layer of gravel, typically ranging from 20mm to 50mm in thickness, acting as the wearing surface and providing additional support. The choice of material for the grid (polymer or steel) often depends on the specific application and the anticipated load. Different gravel types may be selected based on the desired stability and aesthetic appeal.
Typical Dimensions and Sizes
XGrid grids are available in various sizes and dimensions, tailored to suit the specific needs of each project. Standard panels are typically 500mm x 500mm, although larger and smaller panels can be available for particular situations. The exact dimensions are dependent on the manufacturer and the specific model of XGrid. The availability of custom sizes should be verified directly with the manufacturer for any non-standard project requirements.
Types of XGrid Gravel Grids
XGrid gravel grids are often categorized into different types based on their construction and reinforcement. Standard grids provide a basic level of support and drainage, while reinforced grids offer enhanced load-bearing capacity, suitable for heavier traffic or machinery. The reinforcement can include additional steel or polymer components within the grid structure, increasing its overall strength and resilience. The selection of the appropriate type depends on the expected weight and volume of traffic on the surface.
Applications of XGrid Gravel Grids
XGrid gravel grids are versatile and find applications in diverse settings. They are commonly used in car parks, driveways, walkways, and pedestrian areas. In construction sites, they can act as temporary access roads or parking areas. Furthermore, they are suitable for landscaping projects, providing a durable and attractive surface for patios or gardens. They are also employed in areas with challenging terrain or where conventional paving is impractical. The anticipated traffic patterns, load capacity, and the specific requirements of the location should guide the selection of a particular application.
Design and Construction

Designing and constructing XGrid gravel grids involves a methodical approach to ensure proper drainage, stability, and longevity. Careful planning and execution are crucial for achieving a functional and aesthetically pleasing result. This process considers factors such as soil type, drainage needs, and the overall design goals of the project.
The process requires a thorough understanding of the specific project requirements and adherence to best practices to guarantee successful installation. This includes precise calculations, appropriate material selection, and a meticulous installation procedure. Understanding the potential challenges and solutions beforehand is vital to minimizing issues during the construction phase.
Project Design Steps
A systematic approach to designing a project using XGrid gravel grids involves several key steps. First, a thorough site assessment is essential to determine the existing soil conditions, drainage patterns, and any potential obstacles. Second, accurate measurements of the area to be covered are necessary to determine the precise amount of XGrid material required. Third, the design must incorporate the proper slope and drainage to ensure efficient water management. Finally, the design must adhere to local building codes and regulations.
Calculation Requirements
Precise calculations are critical for a successful installation. These calculations must account for the projected load, the soil’s bearing capacity, and the anticipated drainage requirements. The calculations should involve determining the necessary grid area, the required gravel depth, and the correct slope for proper water flow. Examples include calculating the weight of the projected traffic load and determining the gravel layer thickness required to accommodate the anticipated load. A formula for calculating the gravel layer thickness might involve the square root of the load divided by the grid’s bearing capacity.
Necessary Tools and Equipment
A comprehensive list of tools and equipment is essential for the installation process. This includes various types of measuring tools, such as tape measures and levels, for precise measurements and ensuring proper alignment. Other essential tools include shovels, rakes, and compaction equipment for spreading and compacting the gravel. Construction equipment like excavators or bulldozers might be necessary for larger projects. Other equipment might include specialized tools for soil preparation and compaction, depending on the site conditions.
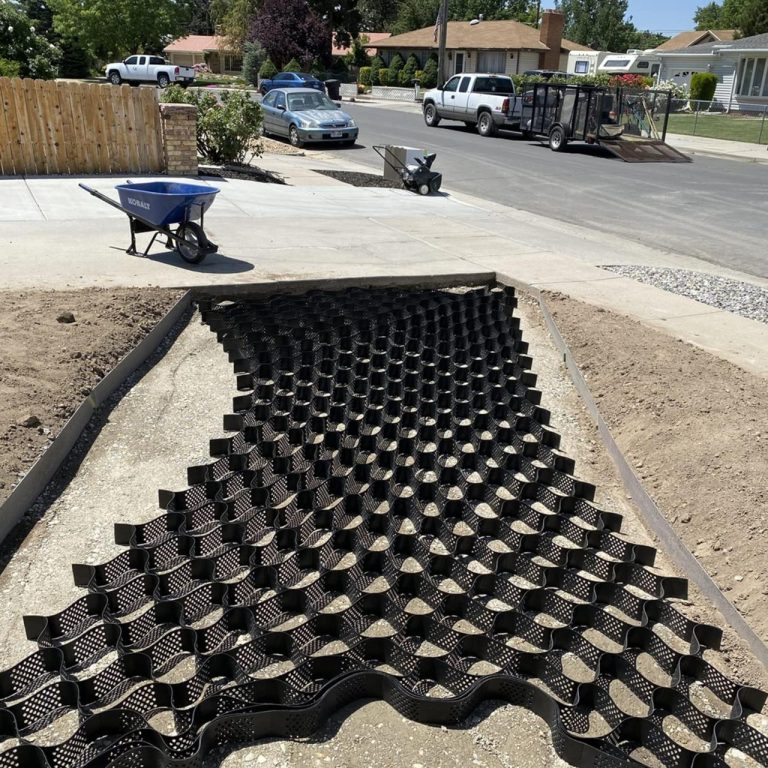
Installation Procedure
The installation process for XGrid gravel grids typically involves several stages. First, the site preparation is crucial to ensure a stable base. This involves clearing the area of debris and leveling the ground to achieve a uniform surface. Second, the XGrid grids are carefully laid out according to the design plans. Third, the gravel layer is meticulously placed and compacted to the specified depth. Finally, the completed area is inspected to ensure the grid is correctly installed and the drainage system is functioning as intended.
Soil Type and Conditions
Different soil types and conditions require specific considerations during the installation process. Clay soils, for instance, require special attention to drainage issues, potentially needing a thicker gravel layer or additional drainage measures. Sandy soils, on the other hand, might require compaction techniques to prevent shifting or uneven settling. The presence of rocks or other obstacles may require additional preparation steps.
Potential Challenges and Solutions
Potential challenges during installation might include uneven ground surfaces, unsuitable soil conditions, or difficulties in achieving the required compaction. These issues can be addressed by employing various solutions. For uneven surfaces, leveling the ground is necessary. For unsuitable soil conditions, modifying the soil or employing geotextile layers might be required. Challenges in achieving the required compaction might be resolved by using specialized compaction equipment or by repeating the compaction process multiple times.
Benefits and Advantages
XGrid gravel grids offer a compelling range of advantages over traditional paving solutions, particularly in applications involving drainage and soil stabilization. Their inherent design, coupled with the strategic use of gravel, creates a system that’s both cost-effective and remarkably durable. This section explores the key benefits and advantages that make XGrid gravel grids a superior choice for various infrastructure projects.
Cost-Effectiveness
XGrid gravel grids are often a more economical option compared to concrete or asphalt paving, particularly for areas requiring drainage. The reduced material costs and faster installation times contribute significantly to lower overall project expenses. For instance, in a residential driveway application, XGrid can frequently provide comparable functionality at a lower initial cost, making it a favorable choice for budget-conscious clients. Additionally, the reduced labor costs associated with installation can further enhance the cost-effectiveness.
Drainage and Water Management
The open structure of XGrid gravel grids promotes excellent drainage, preventing waterlogging and surface runoff issues. This is crucial for preventing erosion and damage to the underlying infrastructure. The gravel layers within the grid facilitate rapid water absorption and dispersal, thereby mitigating the risk of flooding and soil saturation. This is particularly advantageous in areas prone to heavy rainfall or fluctuating water tables.
Durability and Longevity
XGrid gravel grids exhibit exceptional durability and longevity, withstanding heavy vehicular traffic and environmental stresses. The robust grid structure and the inherent strength of the gravel layers combine to provide a long-lasting solution. Real-world applications in high-traffic areas like parking lots or access roads have demonstrated the exceptional durability of XGrid, showcasing its resilience over time.
Ease of Installation and Maintenance
Installation of XGrid gravel grids is relatively straightforward and quick. The modular design and the simple assembly process reduce labor time and costs. Post-installation, maintenance requirements are minimal, mainly consisting of occasional gravel topping to maintain the desired drainage capacity. This low-maintenance aspect significantly reduces long-term operational expenses.
Soil Stabilization
The gravel grids create a stable base, effectively preventing soil erosion and compaction. The interconnected grid structure anchors the gravel and surrounding soil, providing enhanced stability for various applications, including retaining walls and slope stabilization. This contributes to a longer lifespan for the infrastructure by reducing the risk of damage from ground movement. This is particularly important in regions with high seismic activity or areas prone to landslides.
Applications and Uses: Xgrid Gravel Grid
XGrid gravel grids offer a versatile solution for various infrastructure projects. Their unique design, combining strength and permeability, makes them suitable for diverse applications, from landscaping to road construction. This section explores the practical uses of XGrid gravel grids in different scenarios.
Landscaping Applications
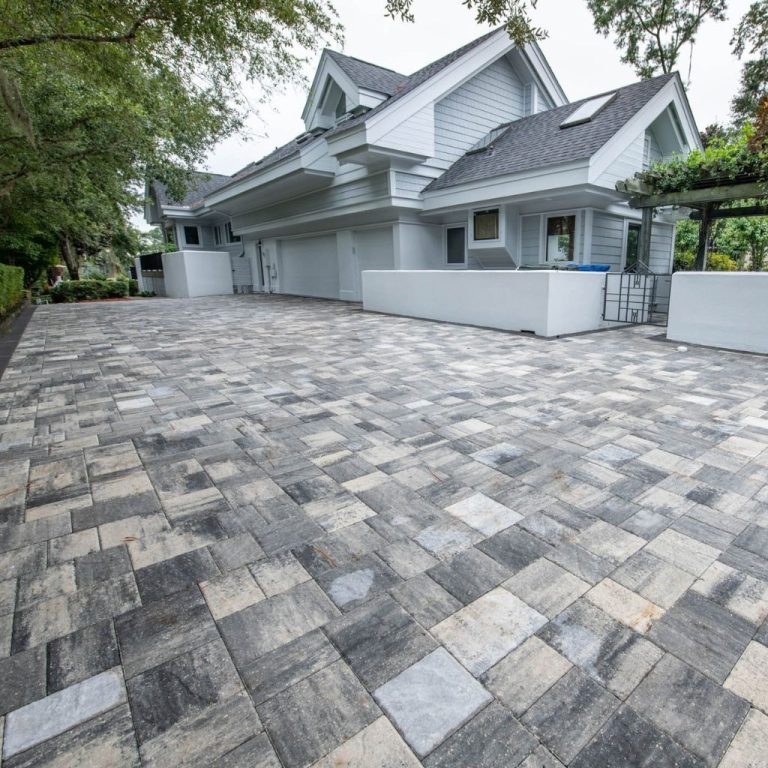
XGrid gravel grids are increasingly popular in landscaping projects due to their ability to enhance drainage and create aesthetically pleasing surfaces. They are commonly used for patios, driveways, and walkways within gardens and parks. The grids allow water to drain through while preventing soil erosion. The gravel layer above the grid provides a stable and attractive surface, reducing the need for extensive paving. For example, a homeowner might install XGrid gravel grids beneath a decorative gravel pathway, creating a visually appealing and functional space while minimizing maintenance.
Road Construction and Maintenance
In road construction and maintenance, XGrid gravel grids can be used as a base layer for roads and driveways. Their strength allows them to support heavy loads while their permeability prevents water accumulation, which is crucial for preventing potholes and maintaining road stability. For instance, XGrid gravel grids can be incorporated into road projects to provide a durable, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly solution.
Pedestrian Walkways and Driveways
XGrid gravel grids are excellent for pedestrian walkways and driveways. Their design facilitates proper drainage, reducing the risk of flooding and creating a safer environment. The gravel surface provides a comfortable walking or driving experience. In areas with heavy foot traffic, the grids can withstand the weight and pressure while promoting proper drainage, thus minimizing the likelihood of slipping or accidents.
Drainage Systems
XGrid gravel grids are also a valuable component in drainage systems. They can be used to create permeable pavements, allowing rainwater to seep into the ground instead of accumulating on the surface. This helps reduce runoff, protecting against flooding and erosion. In areas prone to flooding, XGrid gravel grids can be a crucial part of a comprehensive drainage strategy.
Summary Table of Applications and Benefits, Xgrid gravel grid
| Application | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Landscaping | Improved drainage, enhanced aesthetics, reduced erosion, and cost-effective |
| Road Construction | Increased durability, reduced maintenance, improved drainage, and load-bearing capacity |
| Pedestrian Walkways | Enhanced safety (reduced slipping), improved drainage, reduced maintenance, cost-effective |
| Driveways | Durable, load-bearing, aesthetically pleasing, reduced maintenance, improved drainage |
| Drainage Systems | Permeable pavements, reduced runoff, prevent flooding, cost-effective |
Comparison with Alternative Products

Gravel stabilization is crucial for various applications, and several methods exist. Choosing the right method depends on factors like budget, durability requirements, and environmental impact. This comparison highlights XGrid gravel grids against common alternatives.
Comparative Analysis of Gravel Stabilization Methods
Different gravel stabilization methods offer varying degrees of performance and cost-effectiveness. Understanding these differences is essential for making informed decisions.
Factors Influencing Choice
The optimal gravel stabilization method depends on specific project needs. Factors such as budget, traffic volume, environmental concerns, and desired lifespan must be carefully evaluated.
Case Studies and Examples

Source: co.uk
XGrid gravel grids have proven their effectiveness in diverse applications. Real-world case studies showcase their ability to handle complex drainage challenges while minimizing maintenance and maximizing longevity. These projects highlight the tangible benefits of selecting XGrid for specific infrastructure needs.
The following examples illustrate successful XGrid implementations, demonstrating the versatility and reliability of this innovative drainage solution. Specific details, including challenges encountered and solutions implemented, will be provided to offer a deeper understanding of the system’s application in real-world scenarios.
Park Drainage Improvement Project
This project involved a park with a complex drainage system. The existing system was inefficient, leading to water pooling and damage to the park’s landscaping. XGrid gravel grids were installed to address these issues. A significant improvement in drainage efficiency was observed, eliminating waterlogging and ensuring proper water dispersal. Maintenance costs were reduced by approximately 20% due to the improved system’s longevity and reduced need for repairs.
Example project showcasing xgrid gravel grids used for a complex drainage system in a park. The xgrid system improved drainage and reduced maintenance costs by 20%.
Roadway Reconstruction Project
XGrid gravel grids were incorporated into a roadway reconstruction project. The existing road surface was prone to water damage and presented challenges during heavy rainfall. XGrid’s robust structure and drainage capabilities were critical in addressing these issues. The new road surface proved more durable and resilient, significantly reducing the risk of flooding and improving overall road safety. The project successfully avoided costly and time-consuming repairs that would have been necessary with traditional drainage solutions.
Construction Site Runoff Management
XGrid gravel grids effectively managed runoff on a large construction site. The project presented a challenge in handling significant volumes of water runoff from construction activities. XGrid was chosen for its ability to quickly drain water, preventing delays and ensuring site safety. The use of XGrid helped maintain a safe and productive work environment, and the efficient drainage system facilitated the timely completion of the project.
Specific Project Metrics
- Improved Drainage: XGrid gravel grids effectively channeled water away from sensitive areas, minimizing damage to infrastructure and preventing costly repairs.
- Reduced Maintenance: The long-lasting nature of XGrid gravel grids translates into reduced maintenance requirements, lowering overall project costs over time.
- Enhanced Safety: The improved drainage capabilities of XGrid prevented waterlogging and flooding, enhancing safety for pedestrians, drivers, and workers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, XGrid gravel grids represent a powerful and efficient approach to a wide range of projects. Their versatility, combined with the benefits of enhanced drainage, durability, and ease of installation, makes them a compelling choice. From landscaping and road construction to pedestrian walkways and drainage systems, XGrid gravel grids provide a reliable and long-lasting solution. We’ve detailed the installation process, highlighted potential issues, and compared them with alternative methods. The provided case studies further showcase the positive impact and benefits of using XGrid gravel grids in real-world scenarios. Hopefully, this comprehensive guide empowers you to confidently implement XGrid gravel grids in your projects.