Eco Gravel Grids Sustainable Solutions
Eco gravel grids offer a compelling alternative to traditional paving, providing a sustainable and aesthetically pleasing solution for various applications. These innovative grids are constructed from carefully chosen materials, designed for optimal drainage and water infiltration, while showcasing environmentally friendly attributes. They also present a more cost-effective long-term solution in comparison to other paving methods.
The design and construction of eco-gravel grids vary depending on the specific application. Key components often include permeable materials, like recycled plastic or porous concrete, combined with a strategically placed gravel layer. Different types are available to suit diverse needs, from landscaping and infrastructure projects to pedestrian walkways and driveways. These grids are engineered to seamlessly integrate into various terrains and drainage systems, significantly enhancing permeability and reducing stormwater runoff.
Introduction to Eco Gravel Grids
Eco gravel grids are a sustainable alternative to traditional paving systems. They offer a practical and environmentally friendly solution for various surface applications, promoting efficient water drainage and minimizing environmental impact. Their modular design allows for adaptability and ease of installation, making them a cost-effective choice for projects ranging from small residential areas to large-scale commercial developments.
These systems leverage the benefits of gravel while mitigating some of its drawbacks. By incorporating a structured grid, they ensure stability and prevent the gravel from shifting or becoming compacted. This also aids in better water drainage, critical for reducing runoff and erosion.
Key Components and Materials
Eco gravel grids typically consist of a strong, durable polymer grid structure, often made from recycled or recyclable materials. This grid acts as a support framework for the gravel layer. The gravel itself is often a graded mix of different sizes, offering stability and drainage capabilities. The grid itself can be designed from various materials, including high-density polyethylene (HDPE), polypropylene, or other durable plastics. The gravel can include crushed stone, recycled aggregates, or other similar materials. This combination ensures a strong, permeable surface.
Types of Eco Gravel Grids
Various types of eco-gravel grids are available in the market, tailored to specific needs and applications. These variations are often categorized by the type of grid material, the size and shape of the grid modules, and the specific gravel mix used. The material selection is crucial for durability, resistance to UV exposure, and environmental considerations.
Environmental Benefits
Eco gravel grids offer several environmental advantages. They promote natural water infiltration, reducing runoff and mitigating the risk of flooding. The use of recycled materials in the grid structure can lessen the environmental impact of traditional paving solutions. By allowing water to percolate into the ground, they help replenish groundwater supplies and reduce the strain on existing drainage systems. Their durability often means less maintenance over time, further reducing the environmental impact of pavement upkeep.
Applications
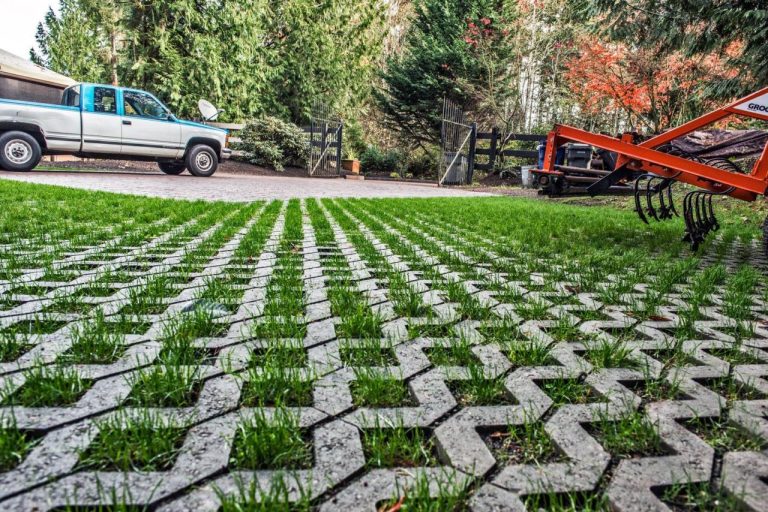
Eco gravel grids are versatile and can be used in a wide range of applications. They are frequently employed in parking areas, driveways, pedestrian walkways, and landscaping projects. They can also be used for creating permeable surfaces in areas where traditional paving might not be suitable. Their adaptability makes them suitable for diverse environments, from residential properties to parks and even in some commercial areas.
Examples
Here’s a table illustrating some common types of eco-gravel grids:
| Type | Materials | Applications | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Eco Gravel Grid | High-density polyethylene (HDPE) grid, graded gravel | Driveways, parking lots, walkways | Cost-effective, good drainage, durable |
| Reinforced Eco Gravel Grid | High-density polyethylene (HDPE) grid with added reinforcement, graded gravel | High-traffic areas, heavy-duty applications | Increased load-bearing capacity, enhanced durability |
| Color-Coated Eco Gravel Grid | High-density polyethylene (HDPE) grid with color coating, graded gravel | Aesthetic landscaping, pedestrian walkways, decorative areas | Enhanced visual appeal, suitable for various design elements |
| Recycled Material Eco Gravel Grid | Recycled plastic grid, recycled aggregates | Environmental projects, sustainable development | Minimized environmental impact, supports circular economy |
Applications of Eco Gravel Grids
Eco gravel grids offer a versatile and sustainable alternative to traditional paving methods. Their adaptability to various terrains and applications makes them suitable for a wide range of landscaping and infrastructure projects, promoting both aesthetics and functionality. They are increasingly popular due to their environmental benefits and cost-effectiveness in specific scenarios.
Common Landscaping Applications
Eco gravel grids excel in landscaping projects due to their ability to integrate seamlessly with natural environments. They facilitate the growth of grass and vegetation while maintaining excellent drainage. Their use in creating permeable walkways and driveways reduces runoff and promotes water infiltration into the ground. This can be particularly beneficial in areas with limited or slow-draining soil conditions.
Infrastructure Project Implementations
Eco gravel grids are finding increasing use in infrastructure projects, offering a sustainable solution for pedestrian walkways, driveways, and parking areas. Their structural integrity makes them suitable for supporting various loads and traffic conditions. In areas prone to flooding or waterlogging, they provide an effective means of managing stormwater runoff, promoting permeable pavements, and reducing the burden on drainage systems.
Use in Different Terrains
The adaptability of eco-gravel grids extends to diverse terrains. Their flexibility allows for installation on slopes, uneven surfaces, and areas with varying soil conditions. Careful consideration of the grid’s load-bearing capacity and the specific terrain characteristics is critical to ensure proper functionality and longevity. For example, in mountainous regions, eco gravel grids can be used to create pedestrian paths, ensuring stability and minimizing erosion.
Drainage Systems and Permeable Pavements
Eco gravel grids are a key component in modern drainage systems and permeable pavements. Their unique structure allows water to infiltrate the ground, reducing surface runoff and promoting groundwater recharge. This helps manage stormwater effectively, reducing the risk of flooding and erosion. They also help maintain a natural hydrological balance, particularly in urban areas where traditional paving methods often lead to increased runoff.
Pedestrian Walkways and Driveways
Eco gravel grids are well-suited for creating pedestrian walkways and driveways. Their aesthetic appeal complements various landscaping styles, enhancing the visual appeal of the area. The permeability of the grid reduces the need for frequent water runoff, improving pedestrian safety and overall site maintenance. Moreover, they offer a practical solution for areas where traditional paving materials might be impractical or cost-prohibitive.
Factors Influencing the Choice of Eco Gravel Grid
Several factors influence the selection of eco-gravel grids for specific applications. These include the intended load capacity, the projected traffic volume, the soil conditions, and the desired aesthetic integration. The availability of different grid sizes and designs also plays a role in meeting specific project requirements. Proper assessment of these factors ensures the chosen grid is suitable for the intended use and the site conditions.
Comparison with Traditional Paving Methods
| Feature | Eco Gravel Grids | Traditional Paving |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Lower, promotes water infiltration, reduces runoff | Higher increases runoff, less permeable |
| Cost | Potentially lower initial cost, lower maintenance costs | Higher initial cost, higher maintenance costs |
| Lifespan | Long, with proper maintenance | Variable, depending on the material and maintenance |
Eco gravel grids offer a more sustainable and cost-effective alternative to traditional paving methods, especially in situations where water infiltration and reduced runoff are priorities.
Environmental Impact

Eco gravel grids offer a significant environmental advantage over traditional paving methods, promoting sustainable urban development and reducing the negative impacts of urban sprawl. Their porous nature allows for superior water infiltration, reducing stormwater runoff and mitigating the risk of flooding. This approach fosters a healthier ecosystem by supporting local biodiversity and enhancing the overall environmental resilience of urban landscapes.
Eco gravel grids contribute to a more sustainable future by minimizing the environmental footprint of construction and maintenance activities. Their design and construction methods often prioritize recycled or locally sourced materials, reducing the need for resource extraction and transportation, thereby lowering the carbon footprint. This approach fosters a more circular economy and helps preserve natural resources.
Environmental Advantages Over Traditional Paving
Traditional paving materials, like concrete and asphalt, are impermeable, leading to increased stormwater runoff and reduced water infiltration. This contributes to flooding, erosion, and water quality issues. In contrast, eco gravel grids, being permeable, allow water to seep into the ground, recharging groundwater reserves and reducing the strain on urban drainage systems. This process also helps maintain the natural hydrological cycle, supporting local ecosystems.
Role in Reducing Stormwater Runoff and Improving Water Infiltration
Eco gravel grids’ permeable nature significantly reduces stormwater runoff, mitigating the risk of flooding. The open structure allows rainwater to infiltrate the ground, recharging groundwater supplies. This process can also reduce the need for expensive stormwater management infrastructure, such as retention ponds and detention basins. This method can be particularly effective in areas prone to flooding or with limited drainage capacity.
Contribution to Sustainable Urban Development
Eco gravel grids play a crucial role in sustainable urban development by promoting environmentally friendly practices. Their use in urban areas can help mitigate the negative impacts of urbanization on natural ecosystems, promoting biodiversity and supporting a more resilient urban environment. The materials used in eco-gravel grids are often recycled or locally sourced, reducing the environmental impact of construction.
Comparison of Carbon Footprint
Eco gravel grids generally have a lower carbon footprint compared to traditional paving materials. The manufacturing processes for eco gravel grids often utilize less energy and fewer resources, resulting in a smaller environmental impact throughout their lifecycle. The use of recycled materials further reduces the carbon footprint associated with material production. The lower transportation needs of locally sourced materials are another contributing factor.
Ecological Benefits in Different Landscapes
The ecological benefits of eco-gravel grids extend to various landscapes. In urban settings, they contribute to improved water quality and reduced flooding risks. In rural areas, they can enhance water infiltration, supporting local ecosystems and preventing soil erosion. Furthermore, they can help maintain natural hydrological cycles and support local biodiversity. These benefits are especially important in areas facing water scarcity or experiencing increased rainfall intensity due to climate change.
Comparison of Environmental Impact Across Paving Materials
| Paving Material | Water Infiltration | Stormwater Runoff | Carbon Footprint | Recycled Material Use | Maintenance Needs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eco Gravel Grids | High | Low | Low | Potentially High | Low |
| Concrete | Low | High | Medium | Low | Medium |
| Asphalt | Low | High | Medium-High | Low | Medium-High |
Note: Carbon footprint values are relative and can vary depending on specific manufacturing processes and material sourcing. Recycled material use can vary significantly based on the source and type of material. Maintenance needs are generally relative to the lifespan of the material.
Cost and Economic Factors
Eco gravel grids offer a compelling alternative to traditional paving materials, but their economic viability depends on careful consideration of upfront costs, long-term maintenance, and potential savings. Analyzing these factors reveals a nuanced picture of their overall cost-effectiveness.
Understanding the relative costs and potential savings is crucial for informed decision-making. Factors such as installation complexity, material availability, and regional labor costs significantly influence the final price tag. Long-term savings often outweigh initial investment, especially when considering the reduced maintenance needs.
Typical Cost Comparison
Eco gravel grids typically have a lower upfront cost compared to concrete or asphalt paving. This difference stems from the lower material costs and the potential for simpler installation procedures, especially in areas with minimal excavation or preparation required. However, this difference can vary depending on the project scale and specific material choices. For instance, high-quality gravel and specialized grid systems might result in a slightly higher initial investment.
Long-Term Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
The long-term cost-effectiveness of eco-gravel grids is often enhanced by their reduced maintenance needs. Unlike traditional paving options, eco gravel grids generally require less frequent repairs and resurfacing. This translates to substantial savings over the lifespan of the project, which can be significant in high-traffic areas. For example, a parking lot using eco gravel grids might require only occasional cleaning and minor repairs, compared to the ongoing patching and sealing necessary for asphalt or concrete.
Cost Savings from Reduced Maintenance
Reduced maintenance needs translate directly into cost savings. The elimination of costly repairs, resealing, and repaving significantly lowers long-term expenditures. In areas prone to heavy traffic or harsh weather conditions, these savings can be substantial. For instance, a residential driveway using eco gravel grids may avoid the recurring expenses associated with crack repair and resurfacing, leading to a considerable return on investment over the long term.
Factors Influencing Installation Costs
Several factors influence the overall installation cost of eco-gravel grids. The complexity of the project, including the size and shape of the area, plays a crucial role. Furthermore, the availability and cost of materials in a specific region can affect the total cost. Labor costs also contribute significantly to the final price, depending on local wage rates and the complexity of the installation process. Proper site preparation, which may involve excavation or grading, can also influence the overall cost.
Return on Investment (ROI) Analysis
The return on investment for eco-gravel grids varies depending on the application and specific circumstances. In applications with high traffic and minimal maintenance needs, the ROI tends to be more favorable. For instance, a parking lot or a driveway in a residential area might yield a faster ROI compared to a less-used pedestrian pathway. Factors like the expected lifespan of the project and the prevailing material costs should be taken into account when assessing the ROI.
Cost Comparison Table
| Feature | Eco Gravel Grids | Traditional Paving (e.g., Asphalt/Concrete) |
|---|---|---|
| Upfront Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
| Maintenance Costs | Lower (occasional cleaning, minor repairs) | Higher (frequent repairs, resurfacing, sealing) |
| Long-Term Savings | Potentially significant due to reduced maintenance | Limited long-term savings if maintenance is extensive |
Case Studies and Examples: Eco Gravel Grid

Source: co.uk
Eco gravel grids, with their diverse applications and environmental benefits, have demonstrated successful implementation across various projects. These case studies showcase the practical application of these systems and highlight the positive outcomes achieved, alongside the challenges encountered and solutions employed. Understanding these real-world examples provides valuable insights into the viability and effectiveness of eco-gravel grids in different contexts.
Successful Implementations in Urban Environments
Eco gravel grids are particularly well-suited for urban areas, offering sustainable solutions for various infrastructural needs. They effectively address challenges related to stormwater management and create aesthetically pleasing, functional spaces.
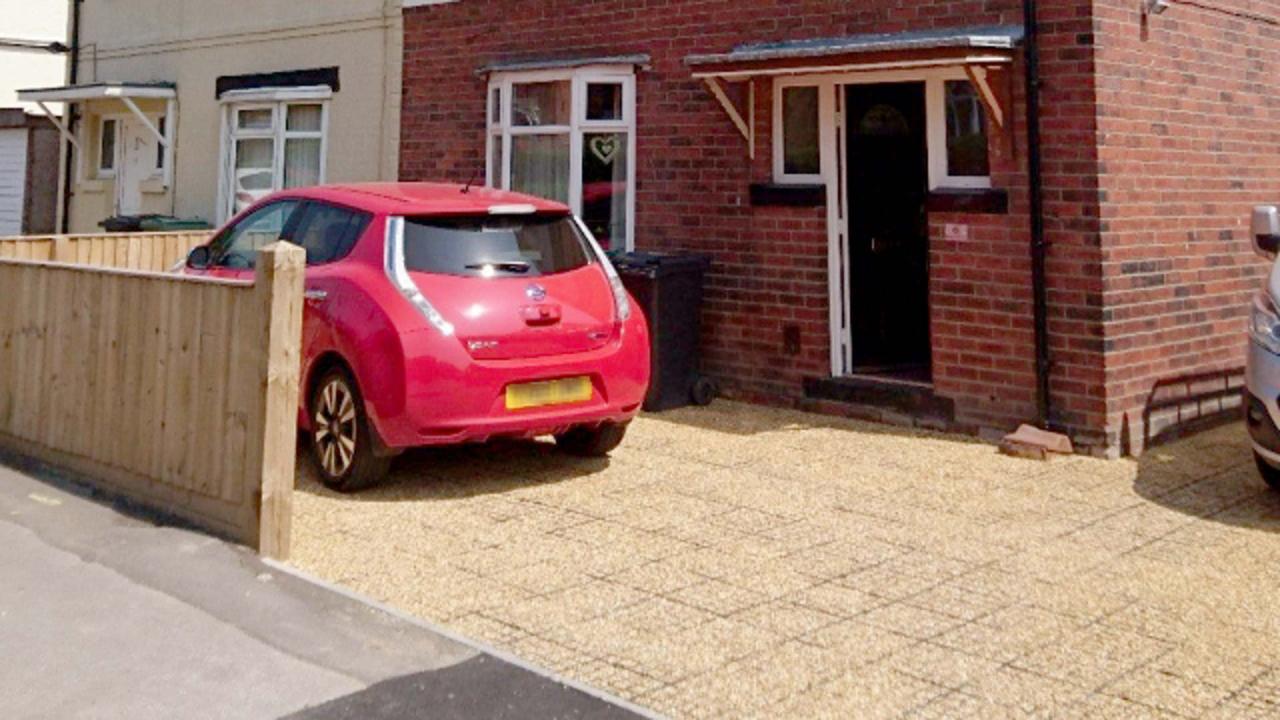
- Park Revitalization Project in Chicago: A revitalization project in a Chicago park incorporated eco-gravel grids to manage stormwater runoff. The system effectively channeled excess water, reducing the risk of flooding and erosion. The grids were integrated seamlessly into the park’s landscape design, enhancing its aesthetic appeal. The project’s success demonstrated the capacity of eco-gravel grids to enhance both functionality and aesthetics within urban spaces.
- Parking Lot Redevelopment in New York City: A parking lot redevelopment project in New York City employed eco-gravel grids to create permeable surfaces. This approach significantly reduced the burden on the city’s drainage system, improving overall stormwater management. The project also involved the use of native plantings, further enhancing the ecological benefits of the eco-gravel grid implementation.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
While eco gravel grids offer numerous advantages, certain challenges may arise during implementation. Careful planning and appropriate solutions are crucial for successful projects.
- Site Preparation and Drainage Issues: Accurate site assessment and proper drainage design are essential for the successful integration of eco-gravel grids. In some instances, the existing infrastructure may require modifications to accommodate the grid’s placement. Implementing proper drainage systems, like diverting excess water to existing channels, resolves these challenges.
- Material Selection and Quality Control: The quality of materials used in eco-gravel grids directly impacts their performance. Selecting high-quality gravel and ensuring proper compaction techniques are vital. Thorough quality control measures and adherence to specifications guarantee optimal results and longevity of the grid system.
Positive Outcomes and Benefits
The use of eco-gravel grids yields significant positive outcomes, impacting both the environment and local communities.
- Improved Stormwater Management: Eco gravel grids effectively manage stormwater runoff, reducing the strain on existing drainage systems and mitigating the risk of flooding. This directly contributes to a healthier urban environment and improved public safety.
- Enhanced Urban Aesthetics: Eco gravel grids seamlessly integrate into urban landscapes, enhancing their aesthetic appeal. The permeable surfaces, coupled with suitable landscaping, create attractive and functional spaces.
- Reduced Infrastructure Costs: In some cases, the implementation of eco-gravel grids can result in lower infrastructure costs compared to traditional solutions. This is due to reduced need for extensive drainage infrastructure and the potential for incorporating the grids into existing spaces.
Summary of Case Studies
| Project Location | Application | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Chicago Park | Park Revitalization | Improved stormwater management, enhanced aesthetics |
| New York City Parking Lot | Parking Lot Redevelopment | Reduced strain on drainage systems, improved stormwater management |
Future Trends and Innovations
The eco-gravel grid industry is poised for significant advancements, driven by increasing environmental awareness and the need for sustainable infrastructure solutions. Emerging trends in materials science and design are promising to enhance performance and sustainability, while ongoing research and development are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. These innovations will undoubtedly impact the future applications of eco-gravel grids in various contexts.
Emerging Trends in Materials
The development of innovative materials is crucial for improving the performance and sustainability of eco-gravel grids. Current research focuses on exploring recycled and bio-based materials as replacements for conventional aggregates. This includes incorporating recycled plastic, wood fibers, or agricultural byproducts into the grid structure. These alternative materials not only reduce the environmental footprint but also potentially enhance the grid’s strength and durability.
Potential Future Developments in Design
Future eco-gravel grid designs will likely prioritize enhanced drainage capabilities and load-bearing capacity. This will involve the integration of optimized geometries and improved interlocking patterns. The incorporation of innovative drainage systems within the grid structure, such as integrated channels or perforations, will further enhance water management and reduce the risk of flooding. This focus on improved drainage will be critical in regions prone to heavy rainfall or flooding.
Enhanced Performance and Sustainability
Enhancements in performance and sustainability will be achieved through material selection and design optimization. For example, incorporating recycled materials can reduce the environmental impact of manufacturing, while optimized geometries can improve load-bearing capacity. The use of bio-based polymers and composites can offer enhanced durability and reduced maintenance requirements. These improvements will directly translate to cost savings and a lower environmental impact over the lifespan of the grid.
Ongoing Research and Development
Ongoing research and development activities are focusing on optimizing the performance of eco-gravel grids under various environmental conditions. This includes investigating the effects of temperature fluctuations, freeze-thaw cycles, and different soil compositions on the grid’s structural integrity and functionality. This research is critical for ensuring the longevity and reliability of these grids in diverse geographical settings. Studies are also exploring the potential for integrating sensors and data acquisition systems into the grids to monitor their performance in real-time.
Potential Future Applications
The versatility of eco-gravel grids makes them suitable for a wide range of applications. Future applications will likely include integration with green infrastructure projects, such as bioswales and rain gardens, to enhance water management in urban areas. The use of these grids in road construction and pedestrian walkways could reduce the environmental impact of traditional construction methods. Their implementation in agricultural settings for drainage and erosion control is also a potential area of growth.
Table: Potential Future Advancements
| Aspect | Design | Materials | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Improved Drainage | Integrated channels, optimized perforations | Porous aggregates, bio-based polymers | Urban stormwater management, agricultural drainage |
| Enhanced Load-Bearing | Advanced interlocking patterns, reinforced structures | Recycled plastic composites, high-strength fibers | Road construction, heavy-duty pedestrian walkways |
| Sustainability | Modular designs for easy assembly and replacement | Recycled and bio-based materials | Green infrastructure projects, eco-friendly construction |
| Monitoring & Control | Integrated sensors, data acquisition systems | Smart materials | Real-time performance monitoring, proactive maintenance |
Final Summary
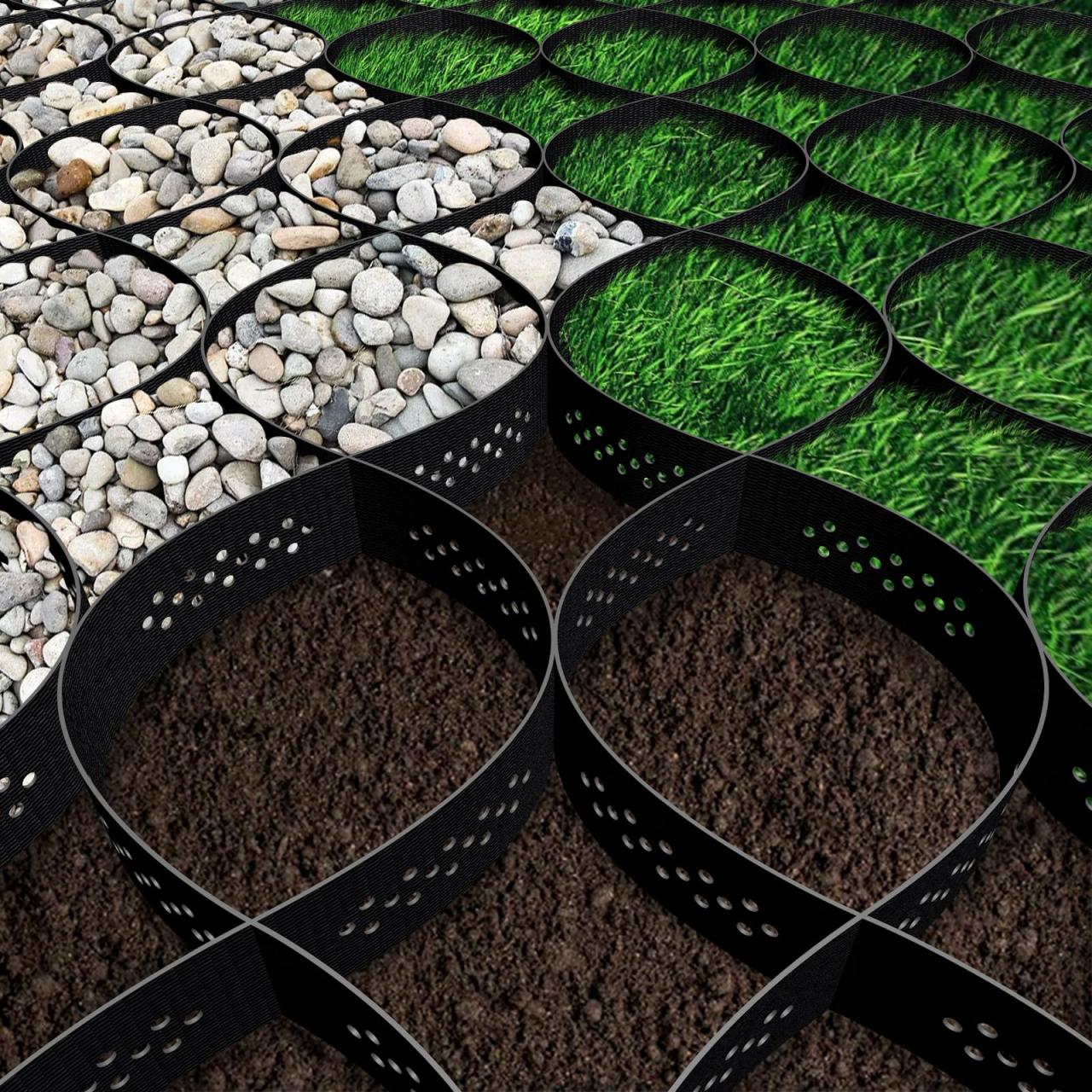
Source: media-amazon.com
In conclusion, eco gravel grids represent a significant advancement in sustainable paving. Their multifaceted applications, from landscaping to infrastructure, demonstrate a remarkable versatility. The environmental benefits, including reduced stormwater runoff and enhanced water infiltration, contribute to a more sustainable urban landscape. The long-term cost-effectiveness, coupled with the ease of maintenance, makes eco-gravel grids a compelling option for diverse projects. Further research and development in materials and design are anticipated to propel eco-gravel grids even further into the future of sustainable urban planning.




